What Is a Container? Container vs VPS, and How to Run Containers on Your VPS
Containers and virtual private servers (VPS) are both powerful technologies used to host applications and services—but they serve different purposes. If you’ve ever wondered what a container is, how it differs from a VPS, and how to use containers on your own VPS, this article is for you.
What Is a Container?
A container is a lightweight, standalone package that contains everything needed to run a piece of software—code, system libraries, runtime, and settings. Containers run on a shared operating system kernel and start in seconds. They're portable, efficient, and consistent across development, testing, and production.
Most containers today are managed using tools like Docker or Podman.
What Is a VPS?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a full virtual machine running on a physical server. It includes its own operating system, file system, and dedicated resources (CPU, RAM, storage). A VPS behaves like a standalone server that you can use to install software, host websites, run applications, and more.
Container vs VPS: What’s the Difference?
Feature | VPS | Container |
|---|---|---|
Operating System | Full OS per VPS | Shares host OS kernel |
Boot Time | Slower (30 sec–1 min) | Fast (milliseconds–seconds) |
Resource Usage | Higher | Lightweight and minimal |
Isolation | Full system-level | App-level |
Use Case | Hosting full services/apps | Running individual services |
In summary:
- A VPS is like a mini virtual server.
- A container is like a mini app environment.
You can run containers inside a VPS to isolate and manage applications more efficiently.
How to Run Containers on Your VPS
If you're using a VPS (e.g., Ubuntu/Debian), follow these steps to install Docker and run your first container.
Step 1: Update the System
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yStep 2: Install Dependencies
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common -yStep 3: Add Docker’s GPG Key
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpgStep 4: Add Docker Repository
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] \
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullStep 5: Install Docker
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -yStep 6: Verify Docker Installation
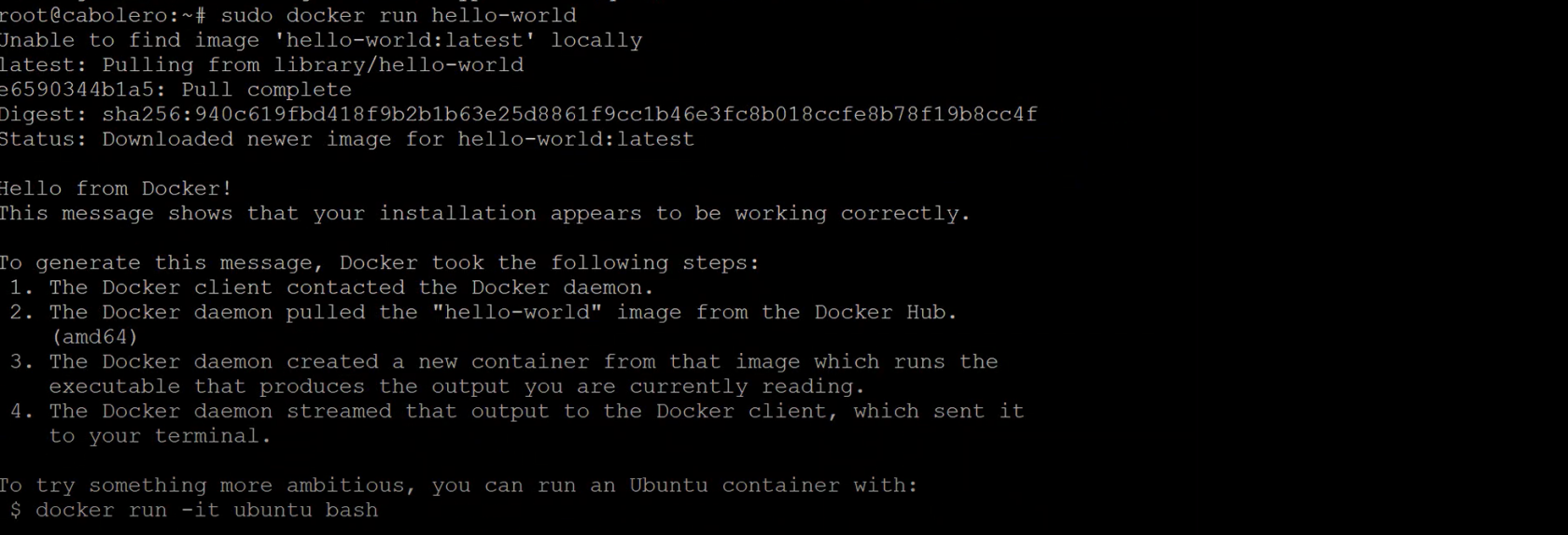
Run the test container:
sudo docker run hello-worldYou should see a message saying Docker is installed correctly.
Run a Web Server in a Container
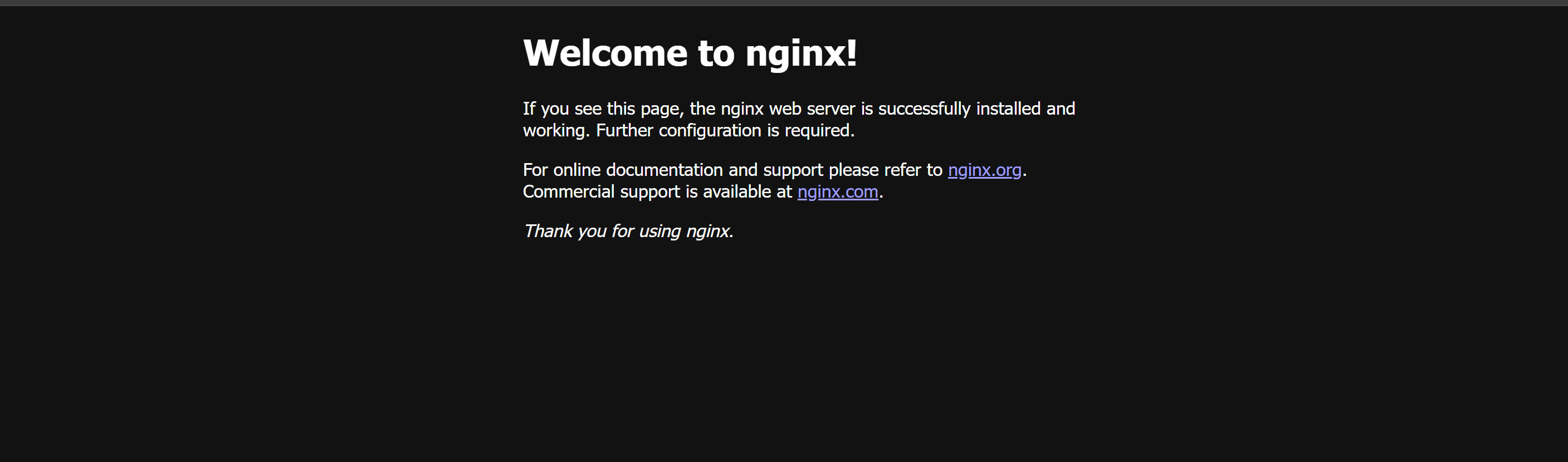
Let’s deploy a basic Nginx web server using Docker:
sudo docker run -d -p 80:80 nginxNow visit your VPS IP address in a browser. You should see the Nginx welcome page—and that means your container is working!
- You can run multiple containers on the same VPS.
- Use Docker Compose to manage complex applications with multiple services.
- Always keep Docker up to date with:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade docker-ce -y